Structure:
Shape ¦ Dimensions ¦ Structure ¦ Home
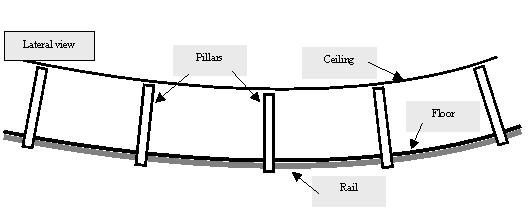
STRUCTURE
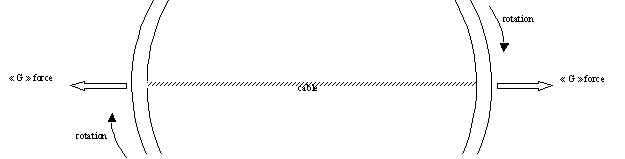
Because
of its rotation that creates a force directed towards its outer edges, the
entire building’s circular shape can be tought of as a hanging structure,
similar to a hanging bridge that is held over a void by cables. However,
instead of having these cables attached to grounded pillars, each cable is
attached to the diametrically opposite point of the structure, which is
itself subject to a force of opposite direction and of equal strength.
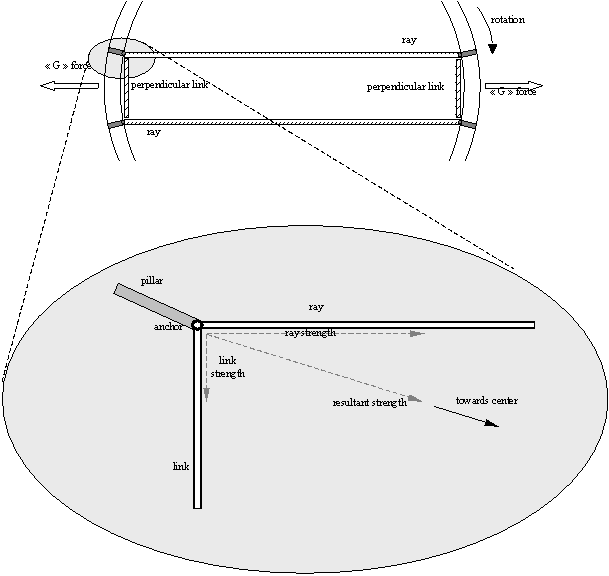
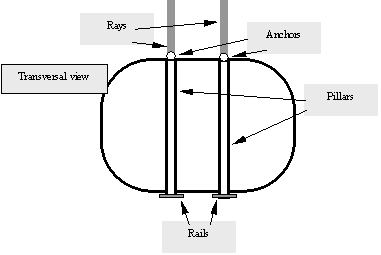
In order to avoid the cables from going through the central section, we
use pairs of parallel cables to link opposite points on the inner side of
the torus. We’ll call these cables “rays”. Perpendicular cables link
the rays at their anchor point with the inner side of the torus, thus
generating a pulling strength towards the center of the structure.
“Vertical” pillars hold the supporting outer edge of the torus (floor)
to the rays anchor point (roof).
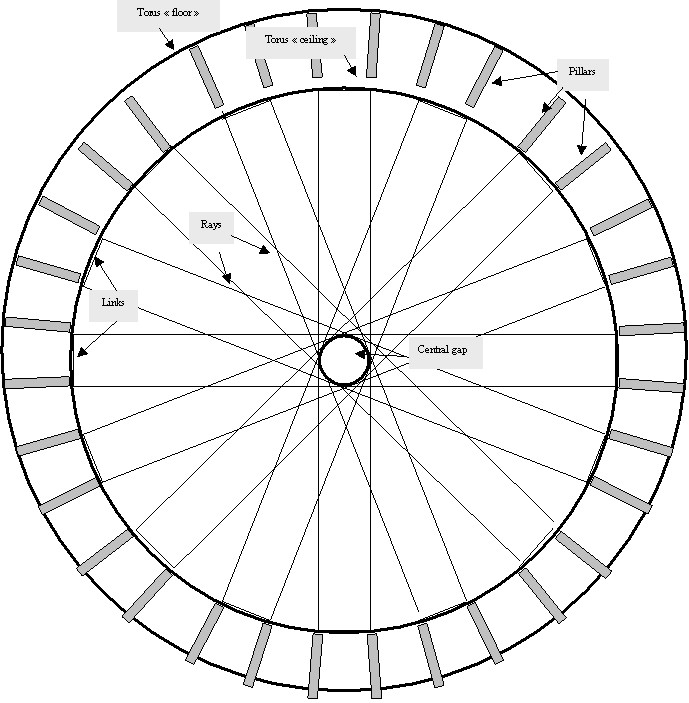
Whilst the illustration shows only one pair, the ideal number of rays is
32 (16 pairs of parallel rays), yielding a 7,8-meter middle area which can
hold the center module.
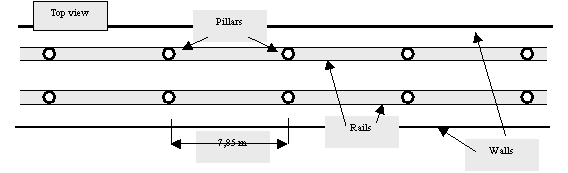
The entire ray-cable-pillar structure will be doubled for sturdiness and
balance. There will therefore be one pair of pillars at every 7.85 linear meter
of torus floor. The pillars will thus hold two rails of understructure running
all around the torus’ floor, over which the remaining of the torus structure
will be built.
ABOUT ELEVATORS
Elevators are two tubes that link the core and the torus. A cabin travels
inside each tube, to shuttle passengers between torus and core.
During its trajectory, the cabin will be subject to a variable
gravitational field g=0,1964*d
in m/s2, where d is the distance between the cabin position at any given
time and the core center in meters. To avoid brutal shock to passengers
moving from a zero-G to a near earth-G environments, the cabin will be
dropped in free-fall when moving from the core to the torus, and decelerated
gradually to reach zero speed simultaneously with the torus level. Similarly,
when the cabin travels from the torus to the core, it will be given an
acceleration until it reaches a speed that will bring it to a still in free
fall when it reaches the core level.
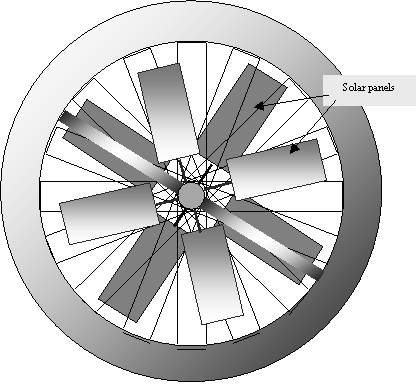
SOLAR PANELS
Electricity will be the main source of energy for the hotel, and will be
provided by solar photovoltaic panels. The panels will be hung off the
central module, radially extending towards the torus, and parallel to the
rays.
Top
¦ Basics ¦ Physics
¦ Dimensions ¦ Structure ¦ 2101
¦ Home






